| Book Title | First Line of Code: Android (Second Edition) |
|---|---|
| Author | Guo Lin |
| Status | Read |
| Summary | Android + Java Development |
First Line of Code: Android (2nd Edition)
Android System Architecture
- Linux Kernel Layer
- System Runtime Library Layer
- Application Framework Layer
- Application Layer
The four main components of Android: Activity, Service, Broadcast Receiver, and Content Provider.
Project Structure#
java folder: Project code
res folder: Project images, layouts, strings, and other resources.
-
Drawable folder: Used to store various types of graphic resources, including but not limited to PNG, JPEG, GIF images, XML-defined drawable resources (such as shapes, selectors, etc.), and nine-patch images. These resources can be used as backgrounds, icons, dividers, etc.
-
Mipmap folder: Mainly used to store application launcher icons. Using the mipmap folder helps ensure that the application icon displays optimally on devices with different resolutions and screen densities.
-
Layout folder: Page layout files
build.gradle app module's gradle build script
AndroidManifest.xml Project configuration file, where all four main components must be registered.
Activity#
- Set Main Activity: Add intent-filter tag and other declarations in the activity tag.
- Add Menu: Build menu resource files and reference them in the activity.
Intent#
Use Intent for activity transitions, starting services, sending broadcasts, etc.
- Explicit Intent: Clearly specifies the activity to start,
- Passing parameters when starting an activity: putExtra -> getStringExtra.
- Returning data to the previous activity: startActivityForResult starts a new activity, using onActivityResult to receive parameters returned when the new activity is destroyed.
- Implicit Intent: By setting the action and category that the current activity responds to in the activity, it can also start activities of other programs (depending on the protocol, supports web pages, phone calls, etc., and passes parameters).
Each Intent can only specify one action but can specify multiple categories.
Lifecycle#
Based on the visibility of the activity and whether it is at the top of the stack, the four states of the activity lifecycle are: Running, Paused, Stopped, and Destroyed.
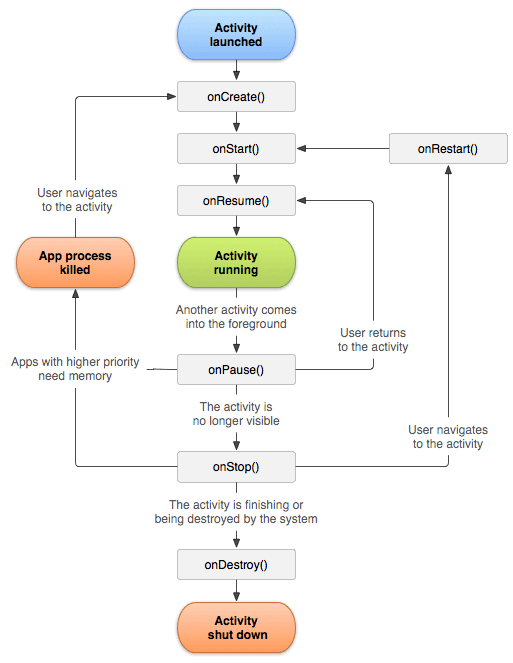
OnSaveInstance: Called before the activity is reclaimed, allowing temporary data to be retained.
- Activity launch modes: standard, singleTop, singleTask, singleInstance.
Page Controls and Layouts#
- Control visibility: visible, invisible, gone
- Layout
LinearLayout: Arranges in a linear direction (horizontal, vertical).
RelativeLayout: Relative positioning allows controls to appear anywhere (relative to the parent layout or the page).
FrameLayout: All controls default to the top left corner.
Percent Layout: PercentFrameLayout and PercentRelativeLayout
Custom Layout: After defining, include it through include;
- Control inheritance structure
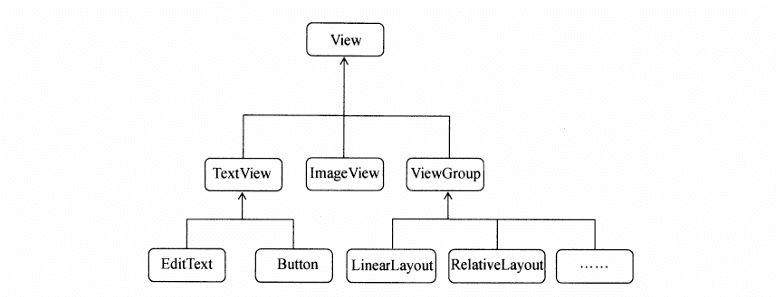
- Custom Controls: Create logic for custom layouts for reuse, dynamically load layout files through inflate.
Fragment#
- UI fragments that can be embedded in activities, each fragment has its corresponding layout file and code file.
- An activity can include multiple fragments, switching fragments through FrameLayout.
- Obtain activity implementation within fragments, communication between fragments and activities, and between fragments.
Fragment Lifecycle#
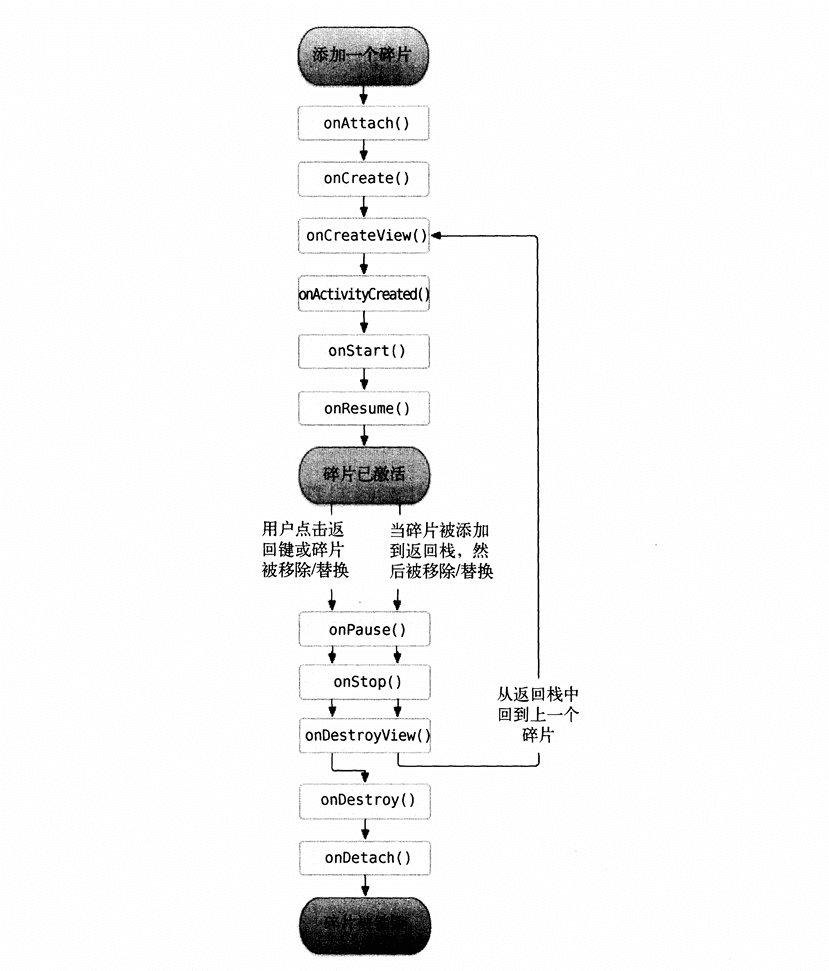
Dynamic Layout Loading#
For example: Use different layouts based on device type (tablet, phone).
- Use qualifiers to correspond to different folder names (can use qualifiers to distinguish size, resolution, orientation).
Broadcast Mechanism#
Can communicate across processes.
- Standard Broadcast: Asynchronous, received simultaneously, cannot be interrupted.
- Ordered Broadcast: Synchronously executed, only one can be received at a time.
Broadcast Types
- Dynamic Registration: Registered in code, needs to be closed promptly after use.
- Static Registration: Registered in AndroidManifest.
For system broadcast reception, some require permission declaration.
Sending Broadcasts
- Standard Broadcast: Custom intent + sendBroadcast method.
- Ordered Broadcast: Custom intent + sendOrderedBroadcast method.
Local Broadcast
Use LocalBroadcast to broadcast locally, using its corresponding sending and receiving methods.
Data Persistence Techniques#
Three data persistence methods in Android.
- Files
- SharedPreferences
- Database
Files#
- Stored in the files folder under the application directory.
- File stream writing (openFileOutput, openFileInput).
SharedPreferences#
Use key-value pairs to store data. Data is stored in package name/shared_prefs/ in XML format.
Storing Data#
- Obtain the sharedPreferences object, use edit() method to get the Editor object.
- Store and retrieve data objects.
- Use apply method to save.
Reading Data#
- Use get method to obtain the corresponding value based on the key.
SQLite#
The book mentions using Android API, SQL statements, and LitePal methods for database operations, and also suggests using Greendao. For comparison, refer to the article below.
Content Provider#
Mainly used to achieve data sharing functionality between different applications.
For example, a phonebook program shares contacts.
Permissions#
Runtime permissions: Authorization for a certain permission during software use.
During development:
- Check if the user has authorized checkSelfPermission.
- If authorized, continue running; otherwise, request authorization requestPermission.
Accessing Data from Other Programs#
- Obtain an instance through getContentResolver.
- Read data.
Creating a Content Provider#
Create a class that inherits from ContentProvider and override the following methods:
- onCreate: Initialization call.
- query: Query, determine which table to query based on the uri parameter.
- insert: Insert.
- update: Update existing data.
- delete: Delete.
- getType: Get the corresponding MIME type for the uri.
Mobile Multimedia#
Notifications#
- Obtain notification instance NotificationManager.
- Create notification object, add Intent to execute notification click action.
- Send.
Camera, Audio, and Video#
Network#
- Use webView to display web pages.
- Use HTTP access HttpURLConnection, OKHttp.
Through OKHttp, you can make GET, POST, and other requests.
- XML Parsing: Pull parsing, SAX parsing.
- JSON Parsing: JSONObject, GSON.
Services#
- Solutions for running programs in the background in Android.
- When the application process is killed, all services dependent on that process will also stop.
Android Multithreading Programming#
Inherit the Thread class.
Implement the Runnable interface.
Write anonymous classes.
Updating UI in Subthreads#
Android does not allow UI updates in subthreads.
Use asynchronous message handling mechanisms to update controls.
Components of asynchronous message handling:
- Message: Messages passed between threads.
- Handler: Sends and processes messages.
- MessageQueue: Message queue that stores all messages from Handlers, only one per thread.
- Looper: Manages the message queue in the thread.
Using AsyncTask:
- onPreExecute: Called before execution.
- doInBackground: Runs in the subthread.
- onProgressUpdate: Responds to UI updates during background publishProgress.
- onPostExecute: Operations after task completion.
Services#
- Defined and started or stopped through Intent (startService, stopService).
- There is only one instance of the service, but each time startService is called, onStartCommand will execute once.
Foreground Service: Add a notification in the service (displayed in the notification bar) and call startForeground.
IntentService: Asynchronous, automatically stops.
Communication Between Activities and Services#
- Build a Binder object, use onBind method in Service.
- Call Binder methods in the activity.
Location-Based Services#
- Apply for API Key and download SDK.
- Permission declaration.
- Obtain location information including: latitude, longitude, address, map.
Material Design#
- ToolBar
- Sliding Menu: The first child control displays the main page content, the second displays Easter egg content.
- NavigationView can customize the top and menu layout in the sliding menu.
- FloatingActionButton: Floating button.
- SnackBar: Provides prompts and adds actionable buttons.
- CoordinatorLayout: Listens to events from all child controls and responds appropriately.
- CardView: Card layout.
- SwipeRefreshLayout: Pull-to-refresh.
Advanced Development#
- Custom Application class to globally obtain Context.
- Implement object serialization through Serializable (serialization implementation) or Parcelabel (decomposing complete objects) interfaces to pass objects via Intent.
- Custom logging tool.
- Create scheduled tasks: Alarm settings implementation.